About Oaks | Map | Plant List | Cultivar/Species Information | Sources | Other Campus Oaks of Interest
Latin Name: Quercus acutissima
Name: Sawtooth Oak
Cultivar:
Family: Fagaceae
Division: Section and Sub-genus: Cerris (neither Red nor White)
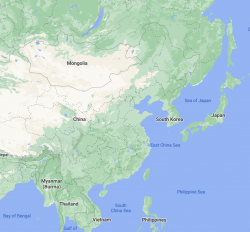
Native range: China, Tibet, Korea, Japan, Indochina, and the Himalayas
Introduced: 1862
Sun/Shade: sun
Height × Width: 40' - 60' × same
Zones: 5-9
Form: Broadly pyramidal in youth; oval rounded to broad rounded with age.
Flower: Monoecious. Staminate (male) pendent catkins
Leaves: 3½ - 7½" × 1 -2¼', i.e. long and narrow, with bristle-like teeth at the ends of the 12-16 pairs of parallel veins. Unlobed. Lustrous and dark green above. Marscescent when young.
Fall color: Clear yellow to golden brown
Fruit: Nut (acorn), cap covers 2/3 of the fruit, and has long spreading and recurved scales
Buds: Pubescent, gray-brown
Bark: Deep ridges and furrows
Wildlife: Food for birds and mammals.
Disease & insect issues: none serious.
Cultural Uses: Charcoal made from Q. accutissima is used in the braisers for heating water for the Japanese tea ceremony.
In South Korea, fruits "processed into a gelatin-like substance, sangsurinamu" ("Wild Food Plants in South Korea; Market Presence, New Crops, and Exports to the United States." Robert W. Pemberton and Nam Sook Lee. Economic Botany, Jan. - Mar., 1996, 50:1, 57-70.)
Folklore:
Notes: WARNING: In the eastern U.S., Q. acutissima has escaped cultivation into nearby forests, imperiling native oak species.
WHERE TO FIND QUERCUS ACUTISSIMA IN MAXWELL ARBORETUM: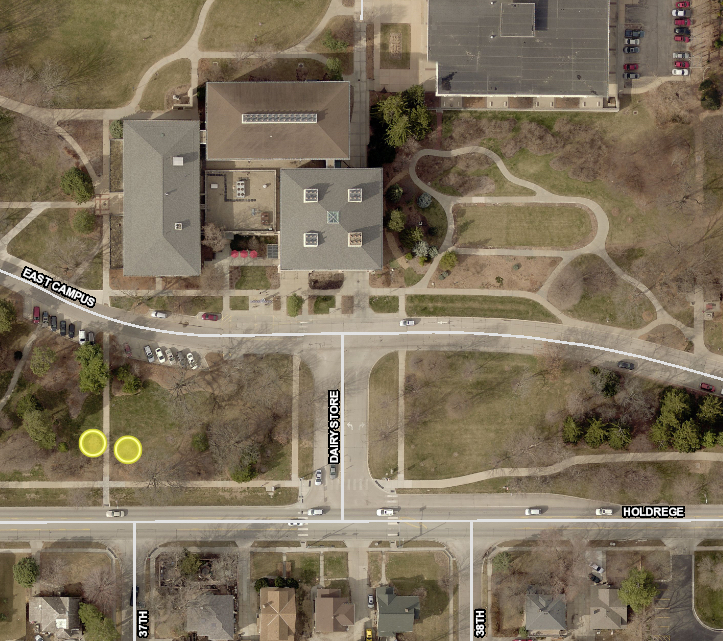
→ NEXT OAK
All images from the Earl G. Maxwell Arboretum unless noted.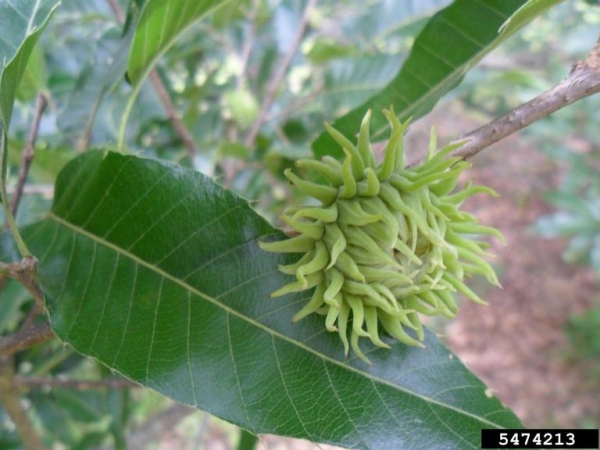
Leaf and Acorn
David Stephens, Bugwood.org
Leaf with serrated margin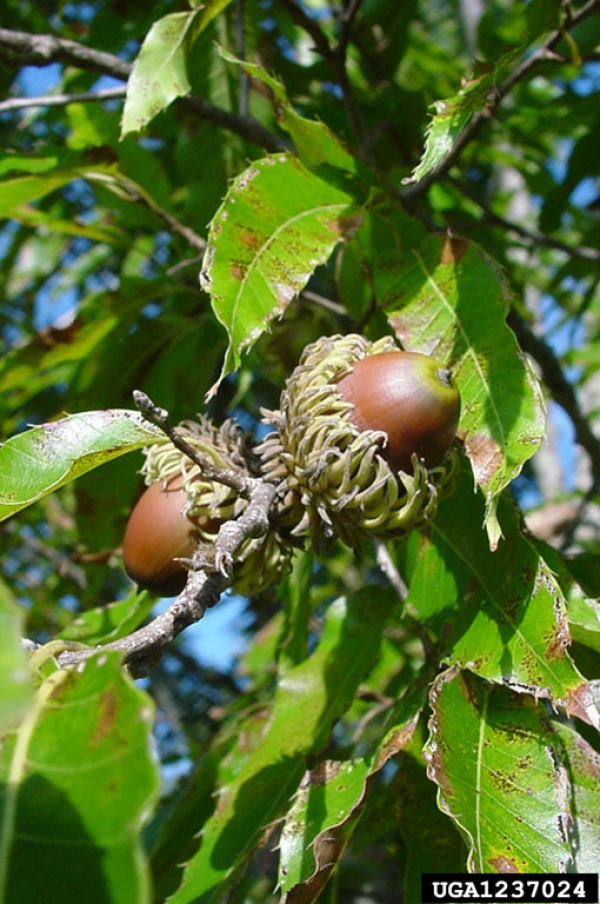
Acorns, almost mature
Chuck Bargeron, University of Georgia, Bugwood.org
Leaves, under side
Hardin Hall
→ NEXT OAK